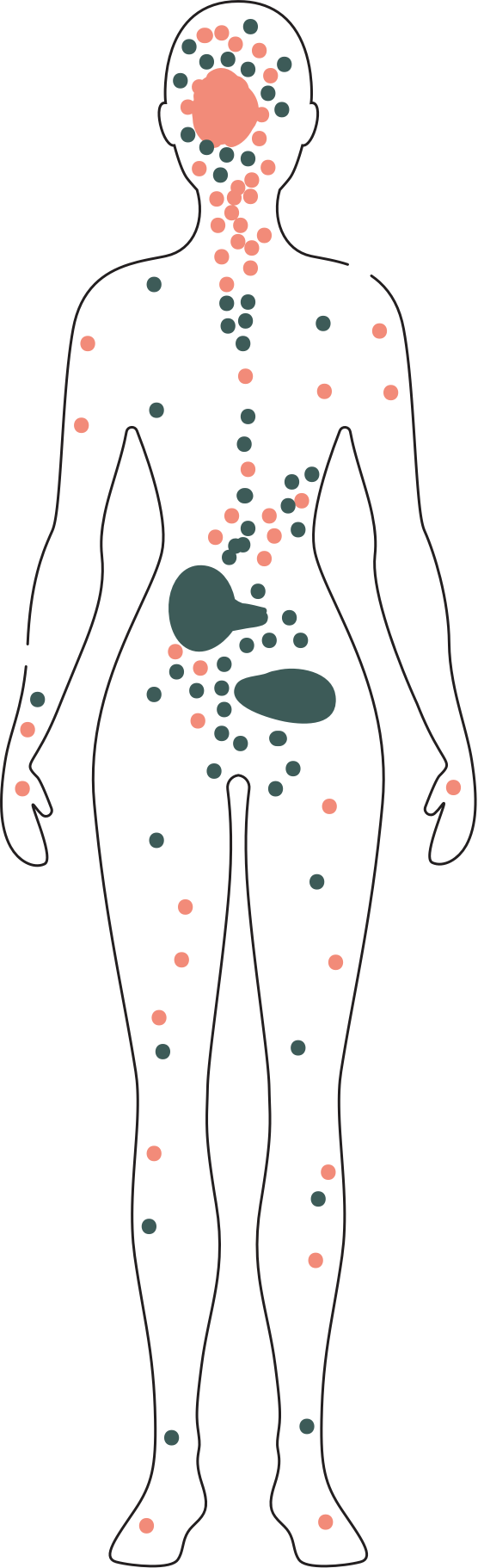
The human body’s endocannabinoid system consists of tiny receptors that play a key role in regulating mood, pain and everyday experience. CBD helps these receptors do what’s needed in order to stimulate all kinds of beneficial changes throughout the body.
A Natural Connection
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a group of receptors found in the immune system, the central nervous system, the brain, organs, connective tissue, and glands. The primary function of the ECS is to maintain a steady, balanced internal state necessary for survival. It is also involved with regulating appetite, sleep, digestion, mood, memory, metabolism, neuro-pro- tection, hormones, and heart function.

CB1 & CB2
The ECS Receptors
Mammals have two types of cannabinoid receptors; cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2). These two components of the endocannabinoid system may sound similar, but they both have unique roles when it comes to how they interact with our bodies.
-
CB1
Most CB1 receptors are found in the brain and spinal cord. Research has shown that CB1 receptors play a role in mood, sleep, and pain sensation. The activation of CB1 receptors is also thought to have neuroprotective benefits.
-
CB2
Most CB2 receptors are found in the immune system, as well as the central and peripheral nervous systems. Activation of these receptors may work to reduce inflammation.
The Entourage Effect
Scientists believe that CBD is more effective when THC is present—a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.” THC is an agonist, while CBD is an antagonist. Simply put, the two work in tandem in our bodies to exert an array of benefits. By taking a full plant extract, your endocannabinoid system may get the support it needs to regulate the bodily systems that impact mood, insomnia, inflammation, and more.